Advanced Calculations: Aggregating Dimensions
- 1. Three situations that dimension aggregations are needed
- 2. Three ways to aggregate dimensions
- 3. Five types of aggregations that can be applied to dimensions
1. Three situations that dimension aggregations are needed
- When blending multiple data sources
- When blending multiple data sources in which the dimensions don’t have a consistent level of detail, Tableau will aggregate the linked dimensions to the same level of detail
- In calculations
- When dimensions are used in calculations with aggregated measures, they must be aggregated
- Tableau can’t mix aggregate and non-aggregate comparisons in calculations
- When you just want to know the aggregation of a dimension
2. Three ways to aggregate dimensions
-
Aggregated in a calculated field
-
Aggregated by right-clicking and dragging the dimension into the view
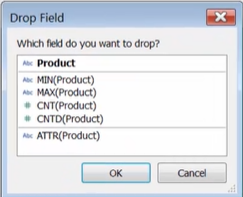
-
Aggregated after they are added to the view by using the context menu
[dimension] field --> drop-down menu --> Attribute / [Measure]
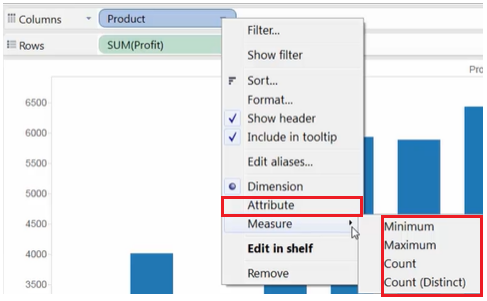
3. Five types of aggregations that can be applied to dimensions
- Minimum [dimension]
- returns the first alphabetic value (the top of the list)
- Maximum [dimension]
- returns the last alphabetic value (the last of the list)
- Count [measure]
- returns the total number of entries in the field
- Count (Distinct) [measure]
- returns the total number of unique entries in the field
- Attribute
- if it has a single value for all rows --> returns the value of the expression
- otherwise --> returns an asterisk (*)
